Python Virtual Machine (PVM)
We know that computers understand only machine code that comprises 1s and 0s. Since computer understands only machine code, it is imperative that we should convert any program into machine code before it is submitted to the computer for execution. For this purpose, we should take the help of a compiler. A compiler normally converts the program source code into machine code.
A Python compiler does the same task but in a slightly different manner. It converts the program source code into another code, called byte code. Each Python program statement is converted into a group of byte code instructions. Then what is byte code? Byte code represents the fixed set of instructions created by Python developers representing all types of operations. The size of each byte code instruction is 1 byte (or 8bits) and hence these are called byte code instructions. Python organization says that there may be newer instructions added to the existing byte code instructions from time to time. We can find byte code instructions in the .pyc file. Following Figure shows the role of virtual machine in converting byte code instructions into machine code:
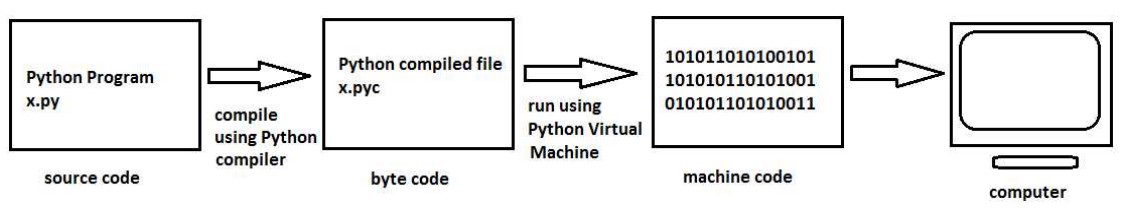
The role of Python Virtual Machine (PVM) is to convert the byte code instructions into machine code so that the computer can execute those machine code instructions and display the final output. To carry out this conversion, PVM is equipped with an interpreter. The interpreter converts the byte code into machine code and sends that machine code to the computer processor for execution. Since interpreter is playing the main role, often the Python Virtual Machine is also called an interpreter.