Python Pandas - Dataframe Operations
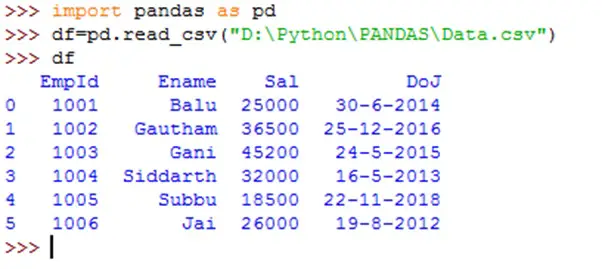
Once we create a data frame, we can do various operations on it.These operations help us in analyzing the data or manipulating the data. First we will create a data frame from a .csv file using read_csv() function as shown below.This data frame will be the basis for our operations.
Dataframe columns and rows count
To know the number of rows and columns available in the data frame, we can use shape attribute. It returns a tuple that contains number of rows and columns as:
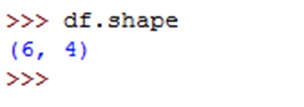
Suppose, we want to retrieve only rows or columns, we can read that number from the tuple as:

Dataframe get rows
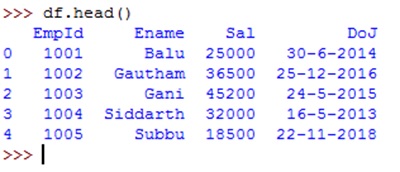
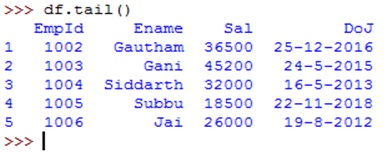
The method head() gives the first 5 rows and the method tail() returns the last 5 rows, as shown below:
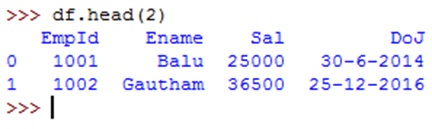
To display only the first 2 rows, we can use head() method by passing 2 to it as:
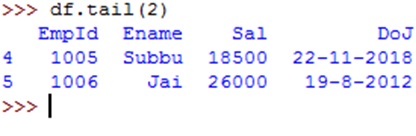
Dataframe rows in range
We can treat the data frame as an object and retrieve the rows from it using slicing. For example, if we write df[2:5], we can get 2nd row to 4th row (excludes 5th row).
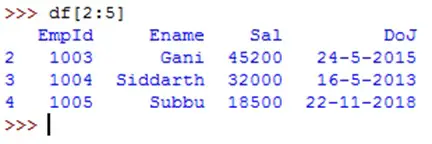
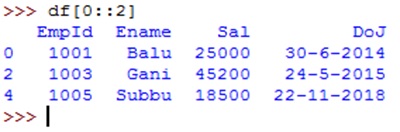
Similarly, to display alternate rows, we can use df[0::2] or df[::2] as shown below:
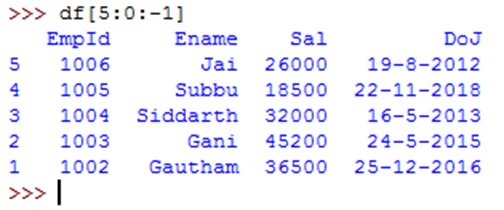
To display the rows in reverse order, we can use negative step size in slicing as:
To Retrieve Column Names To retrieve the column names from the data frame, we can use columns attribute as:

Dataframe columns data
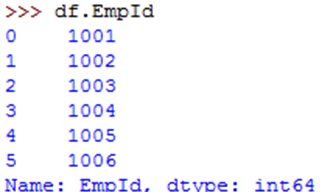
To get the column data, we can mention the column name as subscript.For example, df.empid will display all employee id numbers.This can also be done using df['empid'] which is shown below: